Python List Index
Indexing helps us to get or replace particular element from the list.
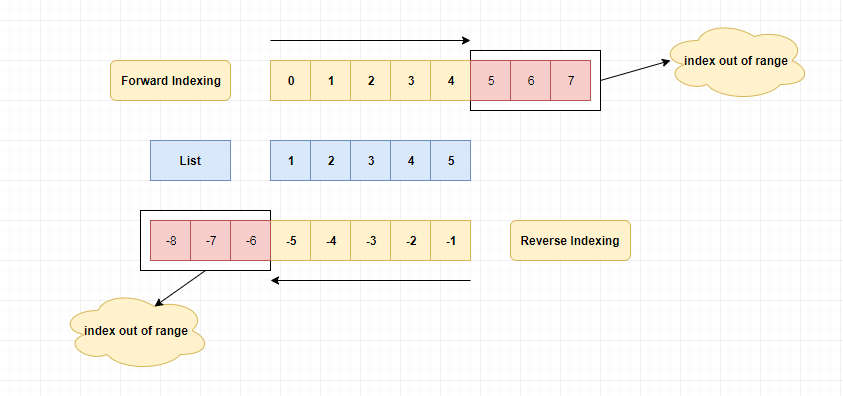
List index also starts from 0.Indexing will return an item.
The list of N element will have the index from 0 to N-1. (Left to Right)
Example
list_name[index]
list_name[0] will return the first item from the list.
list_name[1] will return the second item from the list.
Example
#Python list index numbers = [1,2,3,4,5] print("1st Number ", numbers[0]) print("2nd Number ", numbers[1]) print("3rd Number ", numbers[2]) print("4th Number ", numbers[3]) print("5th Number ", numbers[4])
If the index value exceeds N - 1 (last element's index), it will throw the following error.
IndexError: list index out of range
Example
#Python list index out of range numbers = [1,2,3,4,5] #Above list has 5 elements #index 0 to 4 #Below statements will throw error print(numbers[5]) print(numbers[100])
Indexing in reverse order
We can also access the items from the last.
Like,
list_name[-1] will return the last element from the list.
list_name[-2] will return the second last element from the list.
Pictorial Explanation
Example
#Python list - reverse indexing numbers = [1,2,3,4,5] print("Last element ", numbers[-1]) print("2nd element from the last ", numbers[-2]) print("3rd element from the last ", numbers[-3]) print("4th element from the last ", numbers[-4]) print("5th element from the last ", numbers[-5])
list[0] and list[-0] refers the first element of a list.
Replacing the list elements
As the lists are mutable, we can change its values using index.
Example
#changing list elements numbers = [1, 2, 10, 4, 5] print("List elements are ", numbers) #changing 3rd element as 3. Index 2 numbers[2] = 3 print("New list elements are ", numbers)